By Chris Faubel, MD —
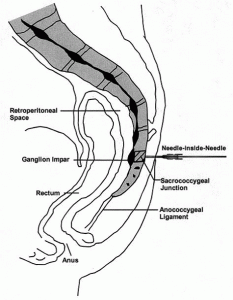
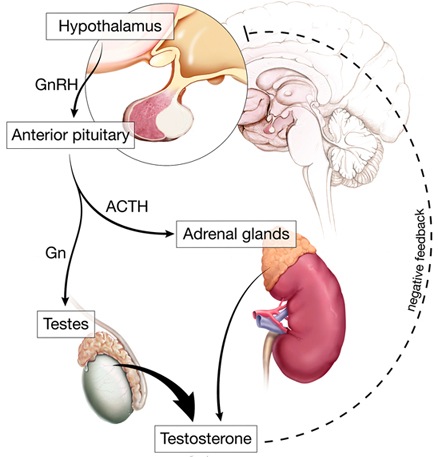
The ganglion impar is a group of sympathetic ganglia which are located anterior to the sacrococcygeal junction; it carries nociceptive signals from the perineum area.
Coccydynia is pain in the area of coccyx (tailbone pain), and is seen frequently in patients with a history of falling directly on their coccyx (tailbone). If the pain does not resolve on its own, and after a course of antiinflammatories and donut cushion, the ganglion impar is blocked under fluoroscopic guidance (or ultrasound guidance).
Billing / Coding
- ICD-9 code: 724.79 (Coccydynia)
- ICD-10 code: M53.3 (Sacrococcygeal disorders, not elsewhere classified)
CPT codes: There is no consensus on the correct code to use. Some use:
- 64530 (Injection, anesthetic agent; celiac plexus, with or without radiologic monitoring).
- 64999 (Unlisted procedure, nervous system) and submit documentation of medical necessity.
- **64520 (Injection, anesthetic agent; lumbar or thoracic paravertebral sympathetic). This one seems the most appropriate, as the sacral sympathetic plexus is just the caudal extension from this lumbar region.
- Note: Fluoroscopic needle guidance is built in to this codes
Procedure technique: (see the pics below for more details)
Position: Prone
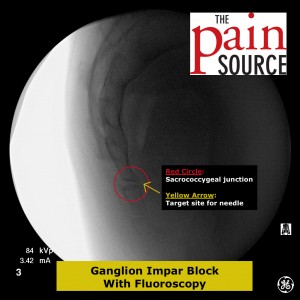
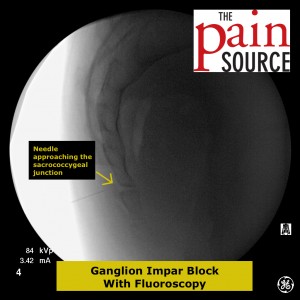
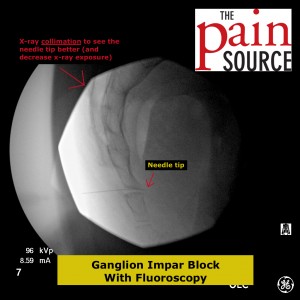
Fluoroscopy: A lateral fluoroscopic view is used to visualize the sacrococcygeal junction.
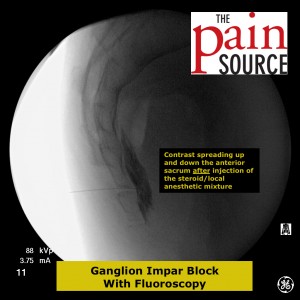
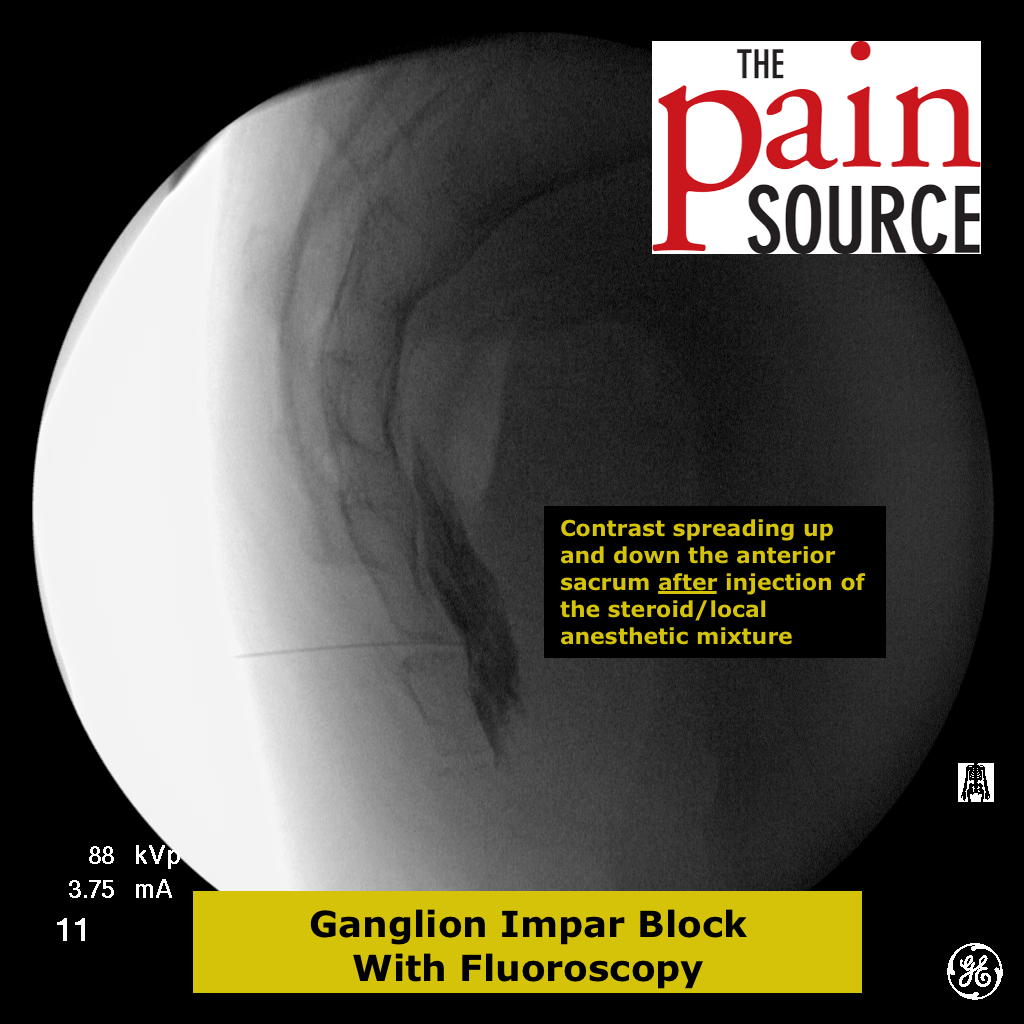
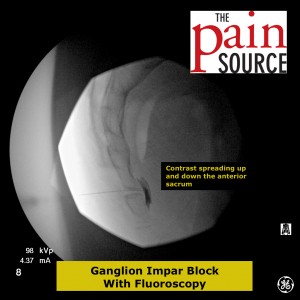
Technique: A 22-25 gauge, 2+-inch needle (I use a 25-gauge, 2-inch) is used to advance through the sacrococcygeal ligament until the needle tip is just barely anterior to the sacrum. Contrast is then injected to visualize correct spread/placement. Finally, a local anesthetic (and sometimes corticosteroid) is injected.
Injectate mixture: 40mg of Kenalog or Depo-Medrol (or 7.2mg of Celestone) with 5+ml of local anesthetic (bupivacaine 0.5%)
Expectations: Patient should have significant reduction in pain within a minute or two if this is the real source of his/her pain; this injection is then both diagnostic and therapeutic.
MORE IMAGES:




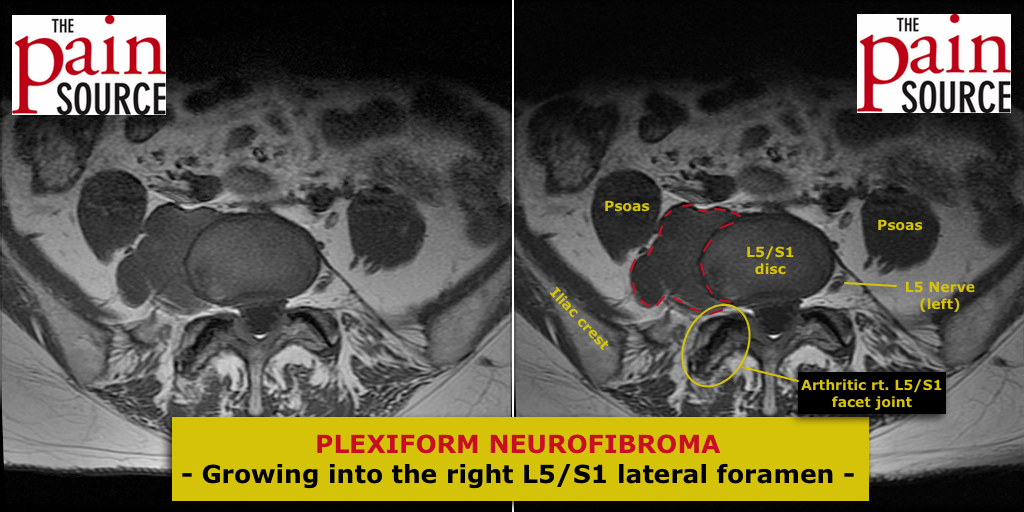

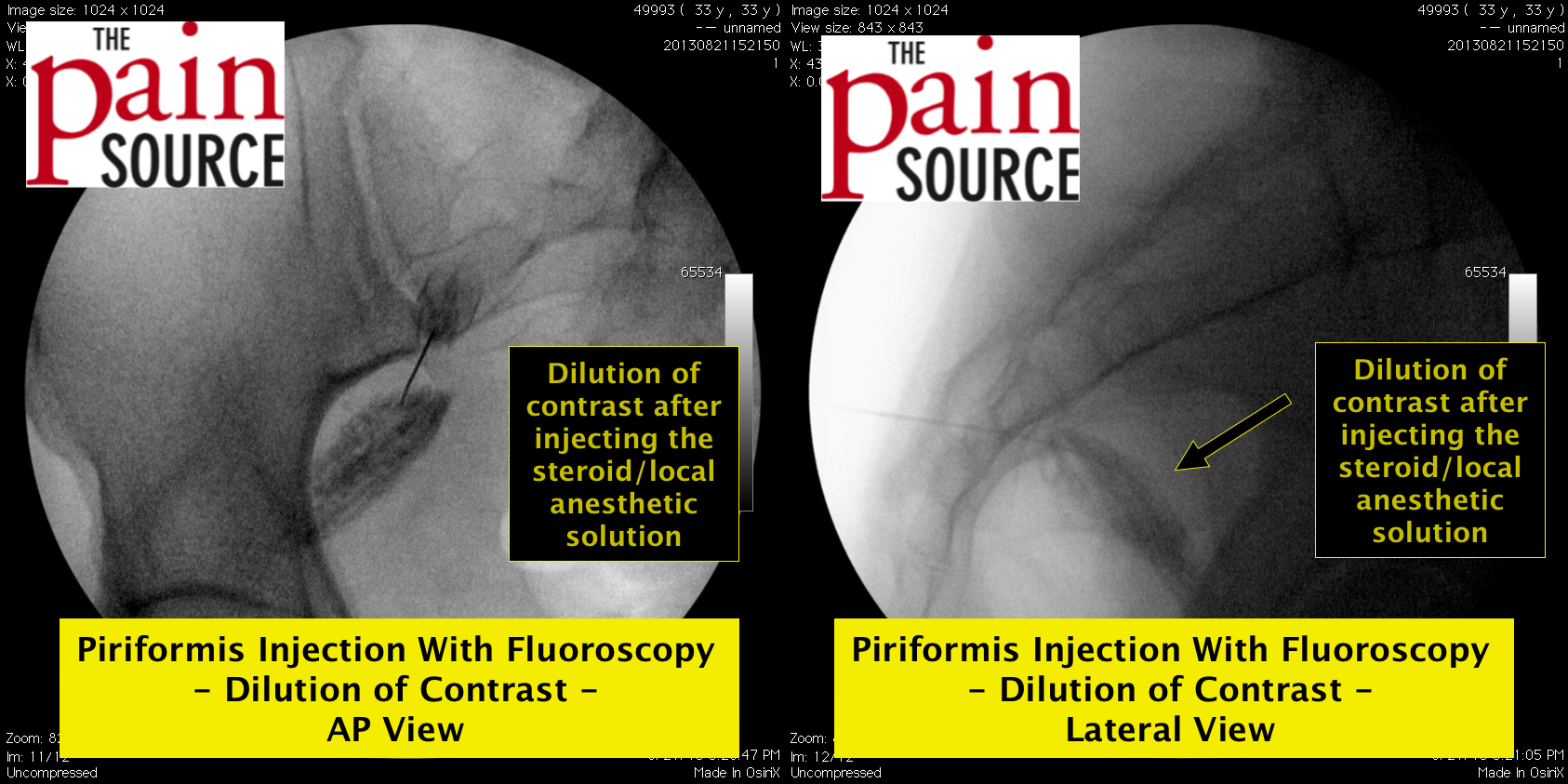
How do you diagnose someone with ganglion impar? MRI?
No MRI. Just a history of falling on your coccyx and chronic pain there. Of course, if acute, an xray should be ordered to rule out a fracture.
Since you include local anesthetic in the injectate, the procedure is both diagnostic and therapeutic.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16924191
Successful injection for coccyx pain.
Foye PM, Buttaci CJ, Stitik TP, Yonclas PP.
excellent article.
Hello,
My mother (58) has coccydynia over 2 years, She tried many types of treatment bat nothing help.
I would like to try “Ganglion Impar Block under fluoroscopy” but we live in Israel. Can you tell me how I can faind someone that may help her.
B.R
Daniel
I don’t know how the health care system works in Israel, but I’d just look for a pain medicine physician over there. I’m sure there are excellent specialists treating pain in Israel, I just don’t know of a specific organization there you could check. Best of luck to your mother.
I heard about this Doc from a friend of mine. He might be worth calling up.
http://www.yashar-pain-clinic.co.il/index.html
I am sorry i meant she. Another way to look for a pain specialist is visit http://www.spineuniverse.com/locate/doctors
do you go right through the ligament in the midline, do you curve the needle, or do you go off lateral to coccyx and then curve underneath it?
Right through the ligament…using fluoroscopy-guidance and contrast to make sure you don’t go too far anteriorly and get into the colon.
Thank you for the original post Chris. I’ve had good luck with this procedure in a patient with intractable perineal/pelvic pain. I’ve also done it going underneath last coccygeal bone aiming cephalad and posterior to place bent needle just along anterior coccyx.
how to know that contrast is not in the rectum?
Because the needle tip is just barely on the ventral side of the sacrococcygeal junction.
I fell onto my coccyx 3 years ago. I still suffer from chronic pain as a result,despite having cortisone injections and coccyx manipulation under general anaesthetic. I have never been offered this procedure and only came across it when looking on the net for help. Will ganglion impar nerve block be beneficial to me as i’m desperate.
I have found these to be HIGHLY effective for relieving coccyx pain (coccydynia) in my patients. You’re gonna have to find an interventional pain specialist and NOT an orthopedic surgeon; they just aren’t trained to perform these.
According to the AMA CPT assistant 2007 the correct code for a ganglion impar is 64999.
does this help pelvic floor pain along with hamstring glut and upper thigh? I have pain and numbness is all these areas after hysterectomy. Ive been injected in SI, hip, hamstring , and bursa this was what was offered to me next. Do the nerves innervate from the sacrum that go to these areas ? Or is this mostly for coccyx pain? I do not have coccyx pain.
I haven’t used this injection to help patients with pelvic floor pain, but have read that it can be helpful for this.
I was curious if you ever thought of changing the layout of your
website? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say.
But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with
it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having one or two images.
Maybe you could space it out better?
Thank you for a very well presented procedure and images. Believe it or not, where I’m working now, we have no fluoro. We have CT and US. Have done these in the past going just under the inferior rim of the coccyx with fluoro as was suggested in another comment. Will give it a go with CT as I feel going through the ligament, as you suggest, is probably more controlled and possibly better tolerated. I wouldn’t feel comfortable using US to get the ganglion as the bone would block visualization. If I just wanted a joint injection at the sc joint, then I could use US… Also, a short block scan of the coccyx region with ct will give me a lot of information about other things that may be going on such as Tarlov cysts, mets, etc.